How to Become an Ultrasound Tech (Sonographer)
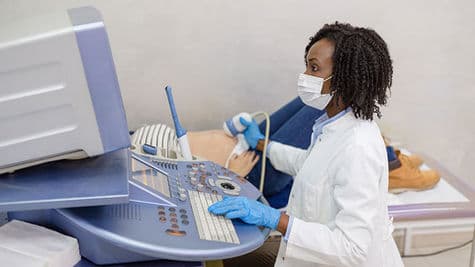
Ultrasound technology allows for safe and non-invasive imaging of the abdomen, providing valuable diagnostic information for healthcare providers.

Ultrasound technology is a rapidly growing field in the medical industry, with increasing demand for qualified ultrasound technicians. Ultrasound Techs use ultrasound to create images of internal organs and tissues, assisting physicians in diagnosing and treating patients. If you're interested in pursuing a career as a sonographer, there are some important steps you'll need to take, including passing the ARDMS exam.
Step 1: Research the Role of an Ultrasound Tech
Before diving into the process of becoming an ultrasound tech, it's essential to understand the role and responsibilities of the job. Ultrasound techs use high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal body structures, such as organs, tissues, and blood vessels. Physicians then use these images to diagnose and treat medical conditions.
Ultrasound techs work in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and private practices. They may specialize in a specific area, such as obstetrics and gynecology, abdominal sonography, or vascular sonography.
Day-to-Day Responsibilities of an Ultrasound Tech

The daily tasks of an ultrasound tech may include:
Preparing patients for procedures by explaining the process and answering any questions
Positioning patients and equipment to obtain the best images
Operating the ultrasound equipment and adjusting settings as needed
Analyzing images to ensure quality and accuracy
Communicating with physicians and other healthcare professionals to discuss findings and assist with patient care
Maintaining patient records and equipment maintenance logs
Clarifying the Terminology: Sonographers vs. Ultrasound Tech
The terms "sonographer" and "ultrasound tech" are sometimes used interchangeably in medical imaging, but the two have important differences.
Sonographers are healthcare professionals who use ultrasound technology to create human body images. They have specialized training in anatomy and physiology, ultrasound physics and instrumentation, and patient care. Sonographers also have a thorough understanding of optimizing ultrasound images for diagnostic purposes, and they work closely with physicians to help interpret and analyze the images.
Ultrasound technicians, on the other hand, may refer to anyone who operates an ultrasound machine, regardless of their level of training or expertise.
As healthcare professionals specializing in using ultrasound technology to create medical images, we are sonographers.
Is It Hard to Pursue a Career as an Ultrasound Tech?
Before choosing ultrasound technology as your career path, key factors to remember are your potential to gain a degree and the job's growth rate in the field. Like many other professions within the medical sector, ultrasound technician jobs are expanding rapidly. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), there's an anticipated increase of 14% in jobs for ultrasound technicians from 2020 to 2030, a rate that surpasses the average growth for all careers. The aging baby-boomer generation requiring diagnostic tests for multiple cardiovascular issues could be the reason behind this hike.
Upon obtaining your degree and certification, opportunities open up to embark on a career in settings such as hospitals, doctor’s offices, or diagnostic laboratories. Many individuals manage to earn a certification after studying for 2-4 years.
In your journey towards becoming an ultrasound tech, most courses focus on science since understanding the human body is essential to operate the sonogram machine effectively. Following the completion of your studies, you become eligible to take the certification exam.
Step 2: Complete an Accredited Ultrasound Tech Program
To become an ultrasound technician, you must complete an accredited training program in diagnostic medical sonography. Attending ultrasound tech school has the potential to be an exceptionally rewarding and enjoyable period of your life, as it offers opportunities for personal and professional growth. However, the crucial factor is selecting an CAHEEP program.
Community colleges, vocational schools, and universities typically offer these programs. Some programs may also offer specialized tracks, such as abdominal sonography or obstetric and gynecologic sonography. Coursework typically covers anatomy and physiology, ultrasound physics and instrumentation, patient care and communication, and image interpretation.
There are many colleges and universities across the United States that offer accredited programs in diagnostic medical sonography, which is the field that includes ultrasound technology. Here is a list of some of the colleges and universities that offer diagnostic medical sonography programs:
University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee
University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
Oregon Tech
Adventist University of Health Sciences
University of Missouri-Columbia
Seattle University
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center
Thomas Jefferson University
University of Alabama at Birmingham
San Diego Mesa College
This is not an exhaustive list, and many other colleges and universities also offer sonography programs. Researching and comparing programs is important to find the one that best fits your needs and goals.
Step 3: Certification
While certification is not required in all states, most employers prefer to hire ultrasound technicians who have earned a professional certification. The American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) offers the most widely recognized certification. To become certified, you must pass the ARDMS exam, designed to test your knowledge and skills in sonography.
Sonography professionals who earn the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) certification meet rigorous criteria in both knowledge and expertise in Sonography. To earn one or more of the following credentials, applicants must meet prerequisites in education and clinical experience and pass ARDMS examinations:
Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographer® (RDMS®)
Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographer® (RDCS®)
Registered Vascular Technologist® (RVT®)
Registered Musculoskeletal™ Sonographer (RMSKS™)
Midwife Sonography Certificate
ARDMS-awarded credentials are widely accepted in the medical community by sonography and vascular professional organizations, as they document personal achievement of recognized professional standards. It is important to note, however, that ARDMS does not validate the day-to-day job performance of any sonography professional.
Obtaining ARDMS certification is a significant achievement in the field of Sonography, as it demonstrates a high level of knowledge and expertise. It also provides opportunities for career advancement and professional recognition. If you're interested in pursuing ARDMS certification, review the prerequisites and requirements carefully and prepare thoroughly for the examinations.
Applying to take the basic Sonography Principles and Instrumentation exam costs $250. Follow-up specialty tests cost $275. Practice tests are available on the ARDMS website.
Other Certification Options
The American Association of Radiologic Technologists administers credentials in sonography and other areas related to medical imaging. Applying for primary certification costs $225.
The Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS) Certification Academy issues credentials for the use of point-of-care ultrasound equipment, i.e., mobile ultrasound imaging systems.
The POCUS Academy online issues a POCUS Fundamentals Certificate as well as certificates for various medical specialties. Obtaining a POCUS certificate costs $150.
Step 4: Job Search and Continuing Education
Once you have completed your training and earned your certification, you will be ready to start your job search. Ultrasound technicians are in high demand, with opportunities in hospitals, clinics, physician's offices, and diagnostic imaging centers. You may also want to consider continuing your education by earning additional certifications or pursuing advanced training in a specialized area of sonography.
In conclusion, becoming an ultrasound technician requires a commitment to education, clinical experience, and certification. By completing an accredited training program, gaining clinical experience, passing the ARDMS exam, and pursuing continuing education opportunities, you can position yourself for a successful career in this dynamic and rewarding field.
After completing an accredited program and obtaining certification, it's time to start your job search. Ultrasound techs can work in a variety of healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and private practices.
Networking with professionals in the field and utilizing job search websites can help you find employment opportunities. It's also beneficial to gain experience in multiple specialties to increase your job prospects.
Sonographers can earn a solid income, especially when compared to other healthcare careers that are possible with an associate degree. As with all jobs, though, income varies across a spectrum. The top 10% of sonographers earn $107,730, in contrast to the bottom 10%, who earn $61,430, according to the BLS’s 2021 data.
Factors that can affect an ultrasound tech's salary include experience, education, certification, and geographic location. Ultrasound techs with more experience and advanced certifications may earn higher salaries.
Highest Paying States for Ultrasound Techs
by Oliur (https://unsplash.com/@ultralinx)
The top-paying states for ultrasound techs in 2020 were:
California: $109,070
Washington: $106,610
Oregon: $103,990
Massachusetts: $103,920
Colorado: $100,480
Ultrasound Tech Specialties and Salaries
As mentioned earlier, ultrasound techs can specialize in various areas, and this can also affect their salary. Here are the median annual salaries for some of the most common ultrasound tech specialties:
Obstetrics and Gynecology: $76,860
Abdominal Sonography: $74,320
Vascular Sonography: $74,320
Breast Sonography: $74,320
Neurosonography: $74,320
Advancement Opportunities for Ultrasound Techs
With experience and additional education, ultrasound techs can advance their careers and increase their earning potential. Some advancement opportunities include:
Lead Sonographer: In this role, you would oversee a team of ultrasound techs and manage the daily operations of the ultrasound department.
Ultrasound Educator: With additional education and certification, you can become an ultrasound instructor at a college or technical school.
Ultrasound Manager: As a manager, you would be responsible for the overall operations of the ultrasound department, including budgeting, staffing, and quality control.
Conclusion
Becoming an ultrasound tech requires dedication, hard work, and a passion for helping others. By completing an accredited program, obtaining certification, and gaining experience in the field, you can embark on a rewarding career as an ultrasound tech. With a competitive salary and job stability, this career path offers a bright future for those interested in healthcare and technology.
Prepry Team
Sonography Educators & Exam Prep Experts
Related Exam Resources
Prepare for your certification with Prepry

