Ultrasound Technologist Earnings: Salary Insights You Need to Know
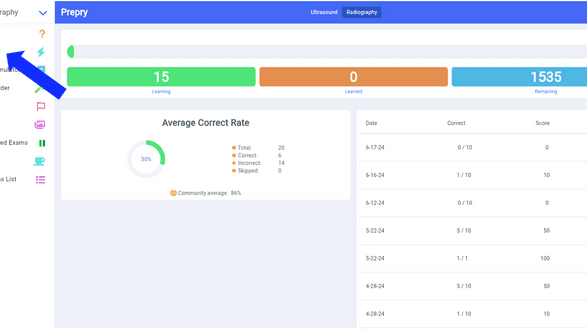
If you’re diving into the world of sonography or radiography, understanding ultrasound technologist earnings is a smart move. Knowing what to expect financially can help you plan your career path, choose specialties, and stay motivated as you prepare for your registry exams. I’m here to break down the salary landscape for ultrasound techs in a clear, friendly way. Let’s explore what influences pay, where the best opportunities lie, and how you can maximize your earning potential....
Read more